M270 PFAS Treatment for Rapid Removal of Contaminants
Your Overview to PFAS Therapy Technologies and Benefits
The frequency of PFAS contamination in water sources requires a comprehensive understanding of readily available therapy modern technologies. Each technology not only targets certain PFAS substances but likewise plays a crucial role in enhancing general water top quality and shielding ecological stability.
Understanding PFAS Contamination
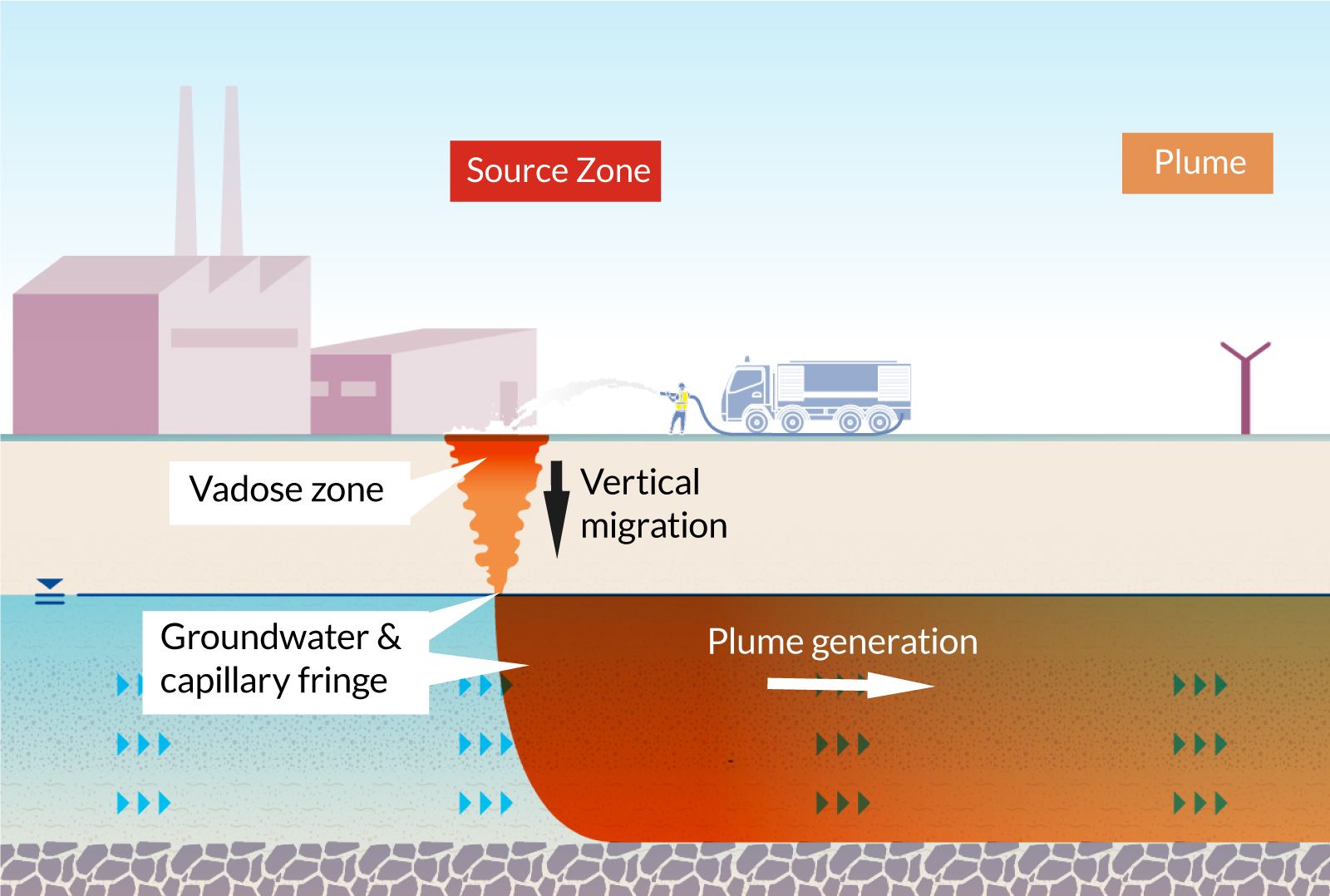
Comprehending PFAS contamination is critical for addressing its pervasive impact on environmental and human health and wellness (m270 pfas treatment). Per- and polyfluoroalkyl materials (PFAS) are a group of artificial chemicals widely made use of in various commercial and customer items because of their water- and grease-resistant residential properties. Typically found in firefighting foams, non-stick pots and pans, and water-repellent textiles, PFAS have gotten in the setting with manufacturing processes, wastewater discharges, and leaching from landfills
As soon as released, these compounds linger in the atmosphere, resulting in widespread contamination of soil and water resources. Their unique chemical structure, characterized by solid carbon-fluorine bonds, makes them resistant to degradation, causing a sensation referred to as "for life chemicals." PFAS can gather in the human body and the food chain, potentially causing damaging health and wellness effects, consisting of immune system interruption, developmental concerns, and a boosted risk of particular cancers.
Regulatory firms and health companies are increasingly acknowledging the value of PFAS contamination, motivating efforts to check, evaluate, and minimize its effects. Recognizing the pathways of PFAS contamination is necessary for informing public law and developing efficient strategies to secure both ecological and human health and wellness.
Summary of Treatment Technologies
Different treatment technologies have actually been established to address the difficulties posed by PFAS contamination in water and soil. These technologies can be extensively categorized right into several groups, each with its special systems and performance in getting rid of PFAS compounds.
One prominent approach is ion exchange, which utilizes resin materials to record and get rid of PFAS from infected water. One more innovation, advanced oxidation processes (AOPs), employs solid oxidants and ultraviolet light to damage down PFAS right into less harmful substances.

Activated Carbon Filtration
Activated carbon filtration is a commonly made use of method for the removal of PFAS from contaminated water, known for its ability to adsorb a wide array of natural substances. This innovation uses activated carbon, an extremely porous material with a substantial surface area, which helps with the binding of PFAS particles via physical adsorption. The efficiency of triggered carbon in eliminating PFAS is influenced by several factors, including the type of carbon utilized, the get in touch with time, and the concentration of PFAS in the water.
One of the benefits of turned on carbon filtering is its adaptability; it can be carried out in different setups, such as granular activated carbon (GAC) systems or powdered activated carbon (SPECIAL-INTEREST GROUP) systems. GAC systems are typically used in larger-scale applications, while political action committee can be utilized in smaller or momentary arrangements. The innovation is relatively very easy to operate and maintain, making it easily accessible for many water treatment facilities.
Ion Exchange Equipment
Ion exchange systems represent another efficient method for the elimination of PFAS from contaminated water, enhancing methods like turned on carbon filtration. These systems run on the principle of trading ions in the water with ions held on a resin product. Ion exchange resins can be especially formulated to target the adversely charged PFAS compounds, properly catching them and permitting cleaner water to travel through.
Among the main benefits of ion exchange systems is their ability to eliminate a wide variety of PFAS, consisting of both long-chain and short-chain variants. This adaptability makes them suitable for different applications, varying from community water treatment to commercial processes. Furthermore, ion exchange systems can usually achieve reduced discovery limits for PFAS compared to some various other therapy methods, therefore boosting water top quality.
However, it is vital to monitor and manage the regeneration of ion exchange media, as the efficiency can decrease over time due to saturation. Appropriate maintenance and replacement of the resin are essential for maintaining the system's performance. Generally, ion exchange systems supply a reliable and efficient remedy for PFAS elimination, contributing substantially to secure alcohol consumption water criteria and ecological defense.
Advanced Oxidation Processes
Advanced Oxidation Processes (AOPs) make use of effective oxidants to effectively degrade PFAS compounds in contaminated water. These cutting-edge therapy approaches generate highly reactive species, such as hydroxyl radicals, that can damage down intricate PFAS particles right into much less dangerous byproducts. m270 pfas treatment. AOPs generally use mixes of ultraviolet (UV) light, ozone, hydrogen peroxide, or Fenton's reagent, boosting the oxidation possibility and enhancing deterioration efficiency
The main benefit of AOPs exists in their capacity to target a wide series of PFAS compounds, consisting of both long-chain pfas management and short-chain versions. This convenience is necessary, as PFAS contamination usually entails blends of different compounds with differing chemical structures. Furthermore, AOPs can be incorporated right into existing water treatment systems, making them a practical remedy for lots of towns and industries.
Nonetheless, the application of AOPs can be resource-intensive, requiring cautious consideration of functional prices and power intake. Furthermore, while AOPs work in breaking down PFAS, they might not completely get rid of all by-products, requiring further therapy steps - m270 pfas treatment. On the whole, AOPs represent an encouraging avenue for resolving PFAS contamination, contributing to cleaner water sources and enhanced public health and wellness protection

Verdict
By choosing the appropriate innovation, areas can improve water top quality, safeguard public wellness, and reduce the ecological risks linked with PFAS exposure. Continued research study and implementation of these techniques are important for effective management of PFAS contamination in impacted areas.